Contents
- 1 Throwing up mucus: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- 1.1 Causes of Throwing up Mucus
- 1.2 Symptoms of Throwing up Mucus
- 1.3 FAQ about topic Throwing up mucus: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- 1.3.1 What causes throwing up mucus?
- 1.3.2 What are the symptoms of throwing up mucus?
- 1.3.3 How is throwing up mucus treated?
- 1.3.4 Can throwing up mucus be a sign of a serious condition?
- 1.3.5 What can I do to relieve throwing up mucus?
- 1.3.6 What causes throwing up mucus?
- 1.3.7 What are the symptoms of throwing up mucus?
- 1.3.8 How is throwing up mucus treated?
Throwing up mucus: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
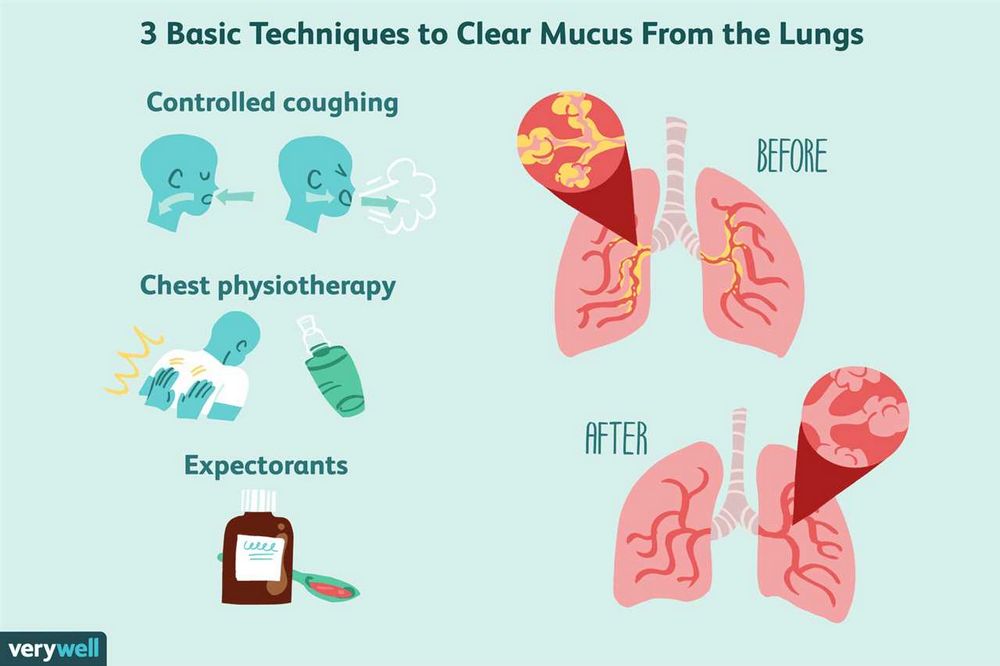
Vomiting is a common bodily response that involves the forceful expulsion of stomach contents through the mouth. While it is often associated with digestive issues, it can also be triggered by respiratory problems. One such condition is coughing up mucus, where individuals expel thick, sticky mucus from their respiratory tract.
Nausea is a common symptom experienced alongside vomiting and coughing up mucus. It is characterized by a feeling of discomfort in the stomach, often accompanied by an urge to vomit. When individuals have excessive mucus production in their respiratory system, it can lead to sputum accumulation, causing irritation and triggering bouts of nausea.
Bronchitis is a respiratory condition that can cause individuals to experience coughing up mucus. It is characterized by inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which results in excessive mucus production. This excess mucus can accumulate and cause discomfort, leading to the need to expel it through coughing or vomiting.
When throwing up mucus becomes a recurring issue, it is important to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can help determine the underlying cause and provide appropriate treatment. Treatment options may include medications to reduce inflammation, antibiotics to treat infections, or lifestyle changes to manage symptoms.
In conclusion, throwing up mucus can be a symptom of various respiratory conditions, such as bronchitis. It is often accompanied by symptoms like coughing, nausea, and excessive mucus production. Seeking medical advice is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of Throwing up Mucus

Throwing up mucus, also known as vomiting mucus or phlegm, can be caused by various factors. Some common causes include:
Nausea: Nausea can lead to throwing up mucus. It is a feeling of unease in the stomach that often precedes vomiting.
Coughing: Persistent coughing can irritate the throat and cause the production of excess mucus. This can eventually lead to throwing up mucus.
Bronchitis: Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which carry air to the lungs. It can cause excessive mucus production, leading to vomiting mucus.
Infections: Certain infections, such as respiratory infections or sinusitis, can cause the body to produce more mucus. This excess mucus can be expelled through vomiting.
Gastrointestinal issues: Conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastritis can cause the stomach to produce excess mucus. This can result in throwing up mucus.
Medications: Some medications, such as certain antibiotics or chemotherapy drugs, can cause nausea and vomiting, which may include the expulsion of mucus.
If you are experiencing frequent or persistent throwing up of mucus, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Respiratory Infections
Respiratory infections are common causes of coughing and throwing up mucus. One of the most common respiratory infections is bronchitis, which is characterized by inflammation of the bronchial tubes. This inflammation can lead to excessive production of phlegm and mucus, causing a persistent cough and the need to clear the throat frequently.
When a person has a respiratory infection, the body’s natural response is to produce more mucus to help trap and remove the invading pathogens. However, excessive mucus production can lead to vomiting, especially if the mucus accumulates in the back of the throat and triggers the gag reflex.
In addition to coughing and throwing up mucus, respiratory infections can also cause other symptoms such as fever, chest congestion, and shortness of breath. These infections can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or other pathogens, and can be spread through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
Treatment for respiratory infections usually involves managing the symptoms and supporting the body’s immune system. This may include over-the-counter cough suppressants, expectorants to help loosen mucus, and plenty of fluids to stay hydrated. In severe cases, antibiotics may be prescribed if the infection is bacterial in nature.
If you are experiencing respiratory infections and are also vomiting mucus, it is important to seek medical attention. This could be a sign of a more serious infection or underlying condition. In some cases, nausea and vomiting may be caused by complications of the respiratory infection, such as pneumonia or bronchial obstruction.
Overall, respiratory infections can be uncomfortable and disruptive, but with proper treatment and care, most people can recover fully. It is important to rest, stay hydrated, and follow any prescribed medications or treatments to help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
Allergies and Sinusitis
Allergies and sinusitis can both cause the production of excess mucus and phlegm in the respiratory system. Allergies occur when the immune system reacts to a substance, such as pollen or pet dander, that is normally harmless. Sinusitis, on the other hand, is an inflammation of the sinuses that can be caused by a viral or bacterial infection, or by allergies.
When allergies or sinusitis are present, the body produces more mucus and phlegm as a defense mechanism. This excess mucus can cause symptoms such as coughing, vomiting, and nausea. The mucus may also be coughed up or vomited up as sputum.
In some cases, allergies and sinusitis can lead to bronchitis, which is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes. This can further increase the production of mucus and phlegm, leading to more severe symptoms.
Treatment for allergies and sinusitis may include antihistamines to reduce allergic reactions, decongestants to relieve congestion, and nasal irrigation to flush out excess mucus. In severe cases, corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation. It is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
| Allergies | Sinusitis |
|---|---|
| Allergies occur when the immune system reacts to a substance. | Sinusitis is an inflammation of the sinuses. |
| Common allergens include pollen and pet dander. | Sinusitis can be caused by a viral or bacterial infection, or by allergies. |
| Allergies can cause symptoms such as coughing and vomiting. | Sinusitis can cause symptoms such as coughing and vomiting. |
| Treatment for allergies may include antihistamines. | Treatment for sinusitis may include decongestants and nasal irrigation. |
Gastrointestinal Issues
Gastrointestinal issues can contribute to the production of excessive sputum or phlegm, leading to coughing and throwing up. Conditions such as bronchitis can cause irritation and inflammation in the airways, resulting in the production of mucus. When this mucus travels down the throat, it can trigger coughing and vomiting.
In addition to respiratory conditions, gastrointestinal problems can also cause nausea and vomiting, which can further exacerbate the production of mucus. Nausea can be caused by various factors, including infections, food poisoning, or digestive disorders.
It is important to address gastrointestinal issues in order to alleviate symptoms of throwing up mucus. Treatment options may include medication to reduce inflammation, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Symptoms of Throwing up Mucus
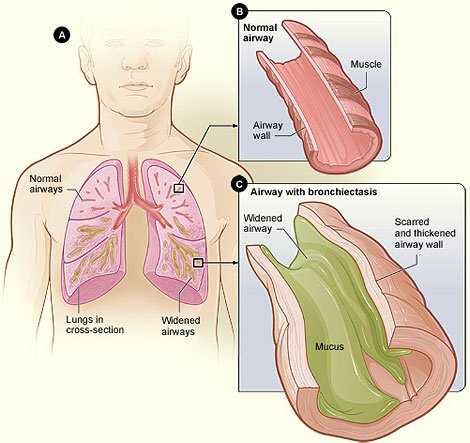
Vomiting or throwing up mucus can be a distressing symptom that may indicate an underlying health issue. When mucus is present in vomit, it can be a sign of various conditions affecting the respiratory system.
Sputum, or mucus, is produced by the respiratory tract and helps to protect the airways from irritants and infections. However, excessive mucus production or the presence of abnormal mucus can lead to symptoms such as coughing, nausea, and vomiting.
One common cause of throwing up mucus is bronchitis, which is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes. In bronchitis, the airways become irritated and produce excess mucus. This can lead to coughing up mucus and, in some cases, vomiting it.
In addition to bronchitis, other respiratory conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and pneumonia can also cause excessive mucus production and vomiting. These conditions may be accompanied by symptoms such as shortness of breath, wheezing, and chest pain.
It is important to note that throwing up mucus can also be a symptom of other non-respiratory conditions, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastrointestinal infections. In these cases, the mucus may be accompanied by other digestive symptoms like heartburn, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.
If you are experiencing symptoms of throwing up mucus, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. The underlying cause of the symptom will determine the specific treatment approach, which may include medications, lifestyle changes, or other interventions.
Coughing and Wheezing
Coughing and wheezing are common symptoms that can occur when throwing up mucus. Coughing is the body’s natural reflex to clear the airways of irritants or foreign substances. When mucus or phlegm builds up in the airways, it can trigger coughing as the body tries to expel the excess mucus.
Wheezing, on the other hand, is a high-pitched whistling sound that occurs when the airways become narrowed or constricted. This can happen due to inflammation or blockage caused by excessive mucus production. Wheezing is often associated with conditions such as bronchitis or asthma.
In addition to coughing and wheezing, throwing up mucus can also lead to other symptoms such as nausea and vomiting. The presence of excessive mucus in the stomach can cause irritation and discomfort, leading to feelings of nausea. In some cases, the body may try to expel the mucus by vomiting.
If you are experiencing persistent coughing, wheezing, or vomiting of mucus, it is important to seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can help determine the underlying cause of these symptoms and recommend appropriate treatment options. In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help reduce mucus production and alleviate symptoms.
FAQ about topic Throwing up mucus: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
What causes throwing up mucus?
Throwing up mucus can be caused by a variety of factors, including respiratory infections, allergies, post-nasal drip, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
What are the symptoms of throwing up mucus?
The symptoms of throwing up mucus can include coughing, wheezing, difficulty breathing, chest congestion, and a feeling of mucus in the throat.
How is throwing up mucus treated?
The treatment for throwing up mucus depends on the underlying cause. It may involve medications to reduce inflammation, antibiotics for infections, or lifestyle changes to manage GERD or allergies.
Can throwing up mucus be a sign of a serious condition?
Throwing up mucus can be a symptom of a serious condition, such as pneumonia or bronchitis. It is important to seek medical attention if you are experiencing persistent or severe symptoms.
What can I do to relieve throwing up mucus?
To relieve throwing up mucus, you can try drinking plenty of fluids, using a humidifier, avoiding irritants like smoke or strong odors, and using over-the-counter medications like expectorants or decongestants.
What causes throwing up mucus?
Throwing up mucus can be caused by a variety of factors, including respiratory infections, allergies, post-nasal drip, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), and certain medications. It is important to consult a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause.
What are the symptoms of throwing up mucus?
The symptoms of throwing up mucus can include coughing, wheezing, chest congestion, difficulty breathing, sore throat, and a feeling of mucus in the throat. These symptoms may vary depending on the underlying cause.
How is throwing up mucus treated?
The treatment for throwing up mucus depends on the underlying cause. It may involve medications to reduce inflammation, antibiotics for bacterial infections, antihistamines for allergies, or lifestyle changes to manage GERD. Drinking plenty of fluids, using a humidifier, and avoiding irritants can also help alleviate symptoms.
I am Lena N. Blackwell, a passionate writer and the author behind the content you find on vpequipments.in.
My work covers a range of topics including babies, culture, food, garden, holidays, pregnancy, tips, and travel. I strive to provide valuable insights and information to help parents, families, and individuals navigate through various aspects of life. My goal is to create content that is not only informative but also engaging and relatable, making your journey a little bit easier and more enjoyable.