Contents
- 1 Can Ear Infection Cause Tooth Pain: Exploring the Connection
- 1.1 The Relationship Between Ear Infections and Tooth Pain
- 1.2 Preventing Ear Infections and Tooth Pain
- 1.3 FAQ about topic Can Ear Infection Cause Tooth Pain? Exploring the Connection
- 1.3.1 Can an ear infection cause tooth pain?
- 1.3.2 How does an ear infection cause tooth pain?
- 1.3.3 What are the symptoms of tooth pain caused by an ear infection?
- 1.3.4 Can tooth pain caused by an ear infection be treated?
- 1.3.5 Is it common for an ear infection to cause tooth pain?
- 1.3.6 Can an ear infection cause tooth pain?
- 1.3.7 What are the symptoms of tooth pain caused by an ear infection?
- 1.3.8 How can I differentiate between tooth pain and ear pain?
Can Ear Infection Cause Tooth Pain: Exploring the Connection

Ear infections are a common ailment that can cause a great deal of pain and discomfort. But did you know that an ear infection can also cause tooth pain? It may seem surprising, but there is a connection between the two.
When an ear infection occurs, it can cause inflammation and swelling in the ear canal. This inflammation can put pressure on the surrounding nerves, including those that are connected to the teeth. As a result, the pain from the ear infection can radiate to the teeth, causing toothaches and discomfort.
In some cases, the pain may be localized to a specific tooth or area of the mouth. This can make it difficult to determine the source of the pain, as it may feel like a toothache rather than an ear infection. However, if you are experiencing tooth pain along with other symptoms of an ear infection, such as earache, fever, or drainage from the ear, it is important to seek medical attention.
Treating the underlying ear infection is key to relieving the tooth pain. Antibiotics are often prescribed to clear up the infection and reduce inflammation. In some cases, over-the-counter pain relievers may also be recommended to help manage the discomfort. It is important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions and complete the full course of antibiotics to ensure that the infection is fully cleared.
In conclusion, while it may seem strange, an ear infection can indeed cause tooth pain. The inflammation and pressure from the infection can radiate to the teeth, causing discomfort and toothaches. If you are experiencing tooth pain along with other symptoms of an ear infection, it is important to seek medical attention to properly diagnose and treat the underlying cause.
The Relationship Between Ear Infections and Tooth Pain
Ear infections can cause tooth pain due to the close proximity of the ear and the teeth. The connection between the two can be explained by the shared nerve pathways in the head and neck region.
When an ear infection occurs, the inflammation and pressure in the ear can radiate to the surrounding areas, including the teeth. This can result in tooth pain that is often described as a dull ache or throbbing sensation.
In some cases, the pain may be localized to a specific tooth or teeth, making it difficult to determine the source of the discomfort. This can lead to misdiagnosis and unnecessary dental treatments.
It is important to note that not all tooth pain is caused by ear infections. Other dental issues, such as cavities, gum disease, or tooth abscesses, can also cause similar symptoms. Therefore, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to accurately diagnose the underlying cause of the pain.
If an ear infection is indeed the cause of tooth pain, treating the infection with appropriate medications, such as antibiotics, can help alleviate the discomfort. Additionally, addressing any dental issues, if present, can also provide relief.
In conclusion, there is a relationship between ear infections and tooth pain. The close proximity of the ear and teeth, as well as the shared nerve pathways, can result in tooth pain when an ear infection occurs. However, it is important to seek professional medical and dental advice to accurately diagnose and treat the underlying cause of the pain.
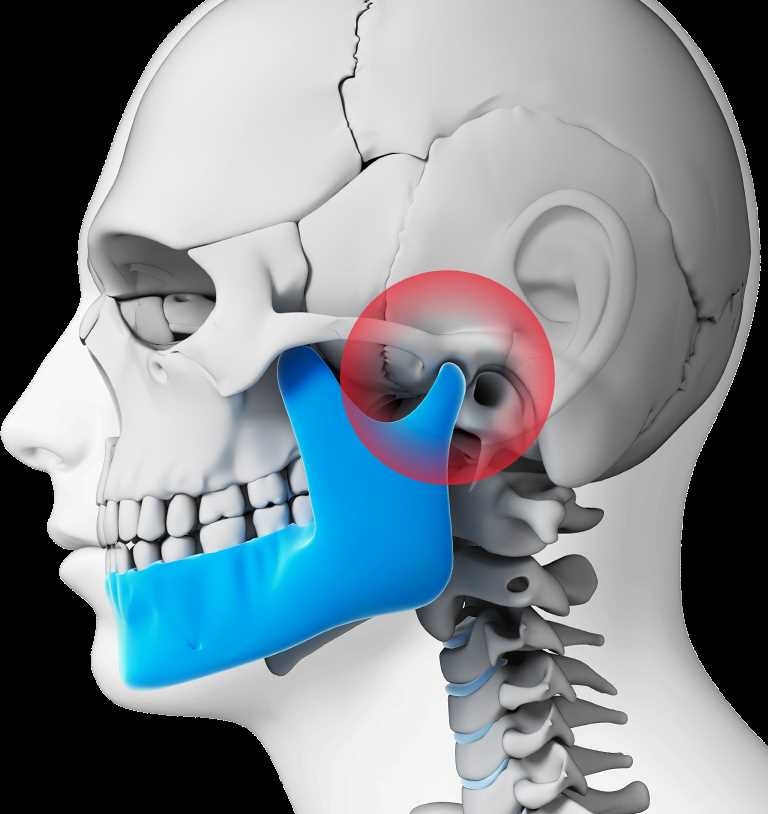
Understanding the Anatomy

The ear is a complex organ that plays a vital role in our ability to hear and maintain balance. It is made up of three main parts: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear.
The outer ear consists of the pinna, which is the visible part of the ear, and the ear canal. The pinna helps to collect sound waves and direct them into the ear canal. The ear canal is a narrow tube that leads to the middle ear.
The middle ear is located between the outer ear and the inner ear. It contains the eardrum, which is a thin membrane that vibrates when sound waves hit it. The eardrum separates the middle ear from the outer ear and helps to transmit sound vibrations to the inner ear.
The middle ear also contains three small bones called the ossicles: the malleus, incus, and stapes. These bones amplify the sound vibrations and transmit them from the eardrum to the inner ear.
The inner ear is the most complex part of the ear and is responsible for converting sound vibrations into electrical signals that can be interpreted by the brain. It contains the cochlea, which is a spiral-shaped structure filled with fluid and tiny hair cells. When sound vibrations reach the cochlea, the hair cells detect the vibrations and send electrical signals to the brain via the auditory nerve.
While the ear is primarily responsible for hearing, it is also connected to other parts of the body, including the teeth. In some cases, an ear infection can cause tooth pain. This is because the nerves that supply the teeth and the ear are connected, and pain signals can be referred between these areas.
Understanding the anatomy of the ear can help us understand how an ear infection can cause tooth pain. When the ear becomes infected, inflammation and pressure can build up in the middle ear. This can put pressure on the nerves that supply the teeth, leading to tooth pain.
In conclusion, the ear is a complex organ that plays a crucial role in our ability to hear and maintain balance. An ear infection can cause pain in the teeth due to the interconnected nerves between the ear and the teeth. Understanding the anatomy of the ear can help us better understand this connection and how it can lead to tooth pain.
Common Symptoms and Overlapping Pain

Ear infections can cause a variety of symptoms, including pain. When an ear infection occurs, the infection can spread to the surrounding areas, such as the teeth and jaw. This can result in tooth pain that is often described as a dull ache or throbbing sensation.
The pain caused by an ear infection can be similar to tooth pain, making it difficult to determine the exact source of the discomfort. In some cases, the pain may radiate from the ear to the teeth, causing confusion and uncertainty for the individual experiencing the symptoms.
Additionally, the nerves in the ear and teeth are connected, which means that pain in one area can be felt in another. This is known as referred pain. Therefore, it is not uncommon for individuals with an ear infection to also experience tooth pain, even if the infection itself is not directly affecting the teeth.
Other common symptoms of an ear infection include earache, fluid drainage from the ear, hearing loss, and a feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear. These symptoms may occur alongside tooth pain, further complicating the diagnosis and treatment of the underlying condition.
If you are experiencing tooth pain and suspect that it may be related to an ear infection, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional. They can evaluate your symptoms, perform any necessary tests, and provide appropriate treatment to address both the ear infection and any associated tooth pain.
Seeking Proper Diagnosis and Treatment

When experiencing tooth pain, it is important to seek proper diagnosis and treatment to determine the underlying cause. While an ear infection can cause pain in the tooth, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to rule out other potential causes.
A dentist will examine the affected tooth and surrounding areas to assess for signs of infection or dental issues. They may also take X-rays to get a closer look at the tooth’s structure and identify any potential problems.
If the dentist determines that the tooth pain is indeed caused by an ear infection, they may recommend a course of treatment. This can include prescribing antibiotics to treat the infection and alleviate the pain. In some cases, the dentist may refer the patient to an ear, nose, and throat specialist for further evaluation and treatment.
It is important to follow the dentist’s recommendations and complete the prescribed treatment to ensure proper healing and prevent any complications. Additionally, maintaining good oral hygiene practices, such as regular brushing and flossing, can help prevent future tooth infections and pain.
If the tooth pain persists or worsens despite treatment, it is crucial to seek further medical attention. This can help identify any underlying issues that may be contributing to the pain and ensure appropriate treatment is provided.
In conclusion, while an ear infection can cause tooth pain, seeking proper diagnosis and treatment from a healthcare professional is essential. By doing so, individuals can address the underlying cause of the pain and receive the appropriate treatment to alleviate their symptoms and promote overall oral health.
Preventing Ear Infections and Tooth Pain
Ear infections can sometimes cause tooth pain due to the close proximity of the ear and the teeth. However, there are steps you can take to prevent ear infections and minimize the risk of experiencing tooth pain as a result.
1. Practice good oral hygiene: Maintaining a proper oral hygiene routine, including brushing your teeth twice a day and flossing daily, can help prevent tooth decay and infections that may contribute to tooth pain.
2. Avoid sharing utensils or personal items: Ear infections can be contagious, so it’s important to avoid sharing items that may spread bacteria or viruses, such as utensils, towels, or toothbrushes.
3. Keep your ears clean and dry: Moisture in the ears can create an environment for bacteria to grow, increasing the risk of ear infections. After swimming or showering, make sure to dry your ears thoroughly with a towel or use a hairdryer on a low setting.
4. Avoid exposure to cigarette smoke: Secondhand smoke can irritate the respiratory system and increase the likelihood of developing ear infections. If you smoke, consider quitting, and try to avoid environments where smoking is prevalent.
5. Stay up to date with vaccinations: Certain vaccinations, such as the pneumococcal vaccine, can help prevent ear infections caused by specific bacteria. Talk to your healthcare provider about recommended vaccinations for you and your family.
6. Practice good hand hygiene: Regularly washing your hands with soap and water can help prevent the spread of bacteria and viruses that can cause ear infections. Encourage proper hand hygiene in children as well.
7. Manage allergies and sinus issues: Allergies and sinus problems can contribute to ear infections. If you have allergies or sinus issues, work with your healthcare provider to develop a management plan that can help reduce the risk of ear infections.
8. Avoid prolonged exposure to loud noises: Loud noises can damage the delicate structures of the ear and increase the risk of ear infections. Use ear protection, such as earplugs or earmuffs, when exposed to loud noises for an extended period.
By following these preventive measures, you can reduce the likelihood of developing ear infections and experiencing tooth pain as a result. However, if you do experience tooth pain or suspect an ear infection, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Maintaining Good Oral Hygiene

Proper oral hygiene is essential for maintaining healthy teeth and gums. While an ear infection may not directly cause tooth pain, it is important to take care of your oral health to prevent any potential dental issues.
Regular brushing and flossing can help remove plaque and bacteria from the teeth and gums, reducing the risk of tooth decay and gum disease. It is recommended to brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss once a day.
In addition to regular brushing and flossing, it is important to visit your dentist for regular check-ups and cleanings. Your dentist can identify any potential dental problems and provide appropriate treatment. They can also offer advice on maintaining good oral hygiene and recommend any necessary dental procedures.
It is also important to be mindful of your diet and avoid consuming excessive amounts of sugary and acidic foods and drinks. These can contribute to tooth decay and erosion, which can lead to tooth sensitivity and pain.
If you experience tooth pain or any other dental issues, it is important to seek prompt dental care. While an ear infection may not directly cause tooth pain, it is possible for dental issues to arise due to the spread of infection or inflammation. Your dentist can evaluate your symptoms and provide appropriate treatment.
| Key Points: |
|---|
| – Regular brushing and flossing are essential for maintaining good oral hygiene. |
| – Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings. |
| – Be mindful of your diet and avoid excessive consumption of sugary and acidic foods and drinks. |
| – Seek prompt dental care if you experience tooth pain or any other dental issues. |
FAQ about topic Can Ear Infection Cause Tooth Pain? Exploring the Connection
Can an ear infection cause tooth pain?
Yes, an ear infection can cause tooth pain. The nerves that supply the teeth and the ears are connected, so when there is an infection in the ear, it can radiate pain to the teeth.
How does an ear infection cause tooth pain?
An ear infection can cause tooth pain because the nerves that supply the teeth and the ears are connected. When there is an infection in the ear, the pain can radiate to the teeth, causing toothache.
What are the symptoms of tooth pain caused by an ear infection?
The symptoms of tooth pain caused by an ear infection may include a dull, throbbing pain in the affected tooth, sensitivity to hot or cold foods and drinks, and pain that worsens when pressure is applied to the tooth.
Can tooth pain caused by an ear infection be treated?
Yes, tooth pain caused by an ear infection can be treated. The underlying ear infection needs to be treated first, usually with antibiotics. Once the ear infection is resolved, the tooth pain should also subside.
Is it common for an ear infection to cause tooth pain?
It is not very common for an ear infection to cause tooth pain, but it can happen. The nerves that supply the teeth and the ears are connected, so when there is an infection in the ear, it can radiate pain to the teeth.
Can an ear infection cause tooth pain?
Yes, an ear infection can cause tooth pain. The nerves that supply the teeth and the ears are connected, so when there is an infection in the ear, it can radiate pain to the teeth.
What are the symptoms of tooth pain caused by an ear infection?
The symptoms of tooth pain caused by an ear infection can include a dull, throbbing pain in the affected tooth, sensitivity to hot or cold foods and drinks, and pain that worsens when you chew or bite down.
How can I differentiate between tooth pain and ear pain?
Differentiating between tooth pain and ear pain can be difficult as the nerves are connected. However, if you experience pain when you move your jaw or open your mouth wide, it is more likely to be tooth pain. On the other hand, if the pain is accompanied by earache, hearing loss, or discharge from the ear, it is more likely to be ear pain.
I am Lena N. Blackwell, a passionate writer and the author behind the content you find on vpequipments.in.
My work covers a range of topics including babies, culture, food, garden, holidays, pregnancy, tips, and travel. I strive to provide valuable insights and information to help parents, families, and individuals navigate through various aspects of life. My goal is to create content that is not only informative but also engaging and relatable, making your journey a little bit easier and more enjoyable.