Contents
Anxiety Medications for Kids: What Parents Should Know

When it comes to the treatment of anxiety in children, parents often have many questions and concerns. While therapy is typically the first line of defense, there are cases where medication may be necessary. If you’re considering anxiety meds for your child, it’s important to understand the role of medication in managing anxiety and what to expect.
Consulting with a child psychiatrist is crucial in determining if medication is appropriate for your child. A psychiatrist will evaluate your child’s symptoms, medical history, and overall well-being to make an informed decision. They will also discuss the potential benefits and risks of medication, as well as any alternative treatments that may be available.
Prescription anxiety meds for kids can help alleviate symptoms and improve their quality of life. These medications work by targeting the brain chemicals that play a role in anxiety. However, it’s important to note that medication is not a cure-all solution. It should be used in conjunction with therapy and other coping strategies to address the underlying causes of anxiety.
Parents should be aware that finding the right medication and dosage may require some trial and error. It’s important to closely monitor your child’s response to the medication and communicate any concerns or side effects to the prescribing psychiatrist. With the right combination of therapy, medication, and support, children with anxiety can lead fulfilling and happy lives.
Understanding Anxiety in Children

Anxiety is a common mental health issue that affects many children. It can manifest in various ways, such as excessive worry, fear, and nervousness. Children with anxiety may have difficulty concentrating, sleeping, and participating in social activities. It is important for parents to understand the signs and symptoms of anxiety in order to provide the necessary support and treatment for their children.
Medication is one option for treating anxiety in children. However, it should not be the first line of treatment. Before considering medication, it is important to consult with a psychiatrist or healthcare professional who specializes in treating children’s mental health. They can assess the severity of the anxiety and recommend the most appropriate course of treatment.
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage anxiety symptoms in children. These medications, commonly referred to as anxiety meds or meds, can help reduce the intensity of anxiety and improve the child’s overall well-being. It is important to note that medication should always be used in conjunction with other forms of treatment, such as therapy or counseling.
Therapy is an essential component of treating anxiety in children. It provides a safe and supportive environment for children to express their feelings and learn coping strategies. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is often used to help children identify and challenge negative thoughts and behaviors associated with anxiety. This type of therapy can be highly effective in reducing anxiety symptoms and improving the child’s quality of life.
It is important for parents to remember that every child is unique, and what works for one child may not work for another. Finding the right combination of medication, therapy, and other treatments may take time and patience. It is also important to monitor the child’s progress and communicate regularly with the healthcare professional to ensure the treatment plan is effective.
In conclusion, understanding anxiety in children is crucial for parents to provide the necessary support and treatment. While medication can be a helpful tool in managing anxiety symptoms, it should always be used in conjunction with therapy and other forms of treatment. By working closely with healthcare professionals, parents can help their children overcome anxiety and lead happy, healthy lives.
Recognizing the Signs of Anxiety

Anxiety is a common mental health condition that can affect people of all ages, including kids. It is important for parents to be able to recognize the signs of anxiety in their children so that they can seek appropriate help and support.
Some common signs of anxiety in kids include excessive worry or fear, restlessness, irritability, difficulty concentrating, trouble sleeping, and physical symptoms such as headaches or stomachaches. These symptoms may vary from child to child, and it is important to remember that not all children will display the same signs.
If you suspect that your child may be experiencing anxiety, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a pediatrician or psychiatrist. They can help determine if your child’s symptoms are related to anxiety and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Treatment for anxiety in children may involve a combination of therapy and medication. Therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can help children learn coping strategies and develop skills to manage their anxiety. In some cases, a psychiatrist may prescribe medication to help alleviate symptoms of anxiety.
It is important for parents to remember that each child is unique and may require an individualized approach to treatment. Working closely with healthcare professionals can help ensure that your child receives the best possible care for their anxiety.
Impact of Anxiety on Children’s Mental Health
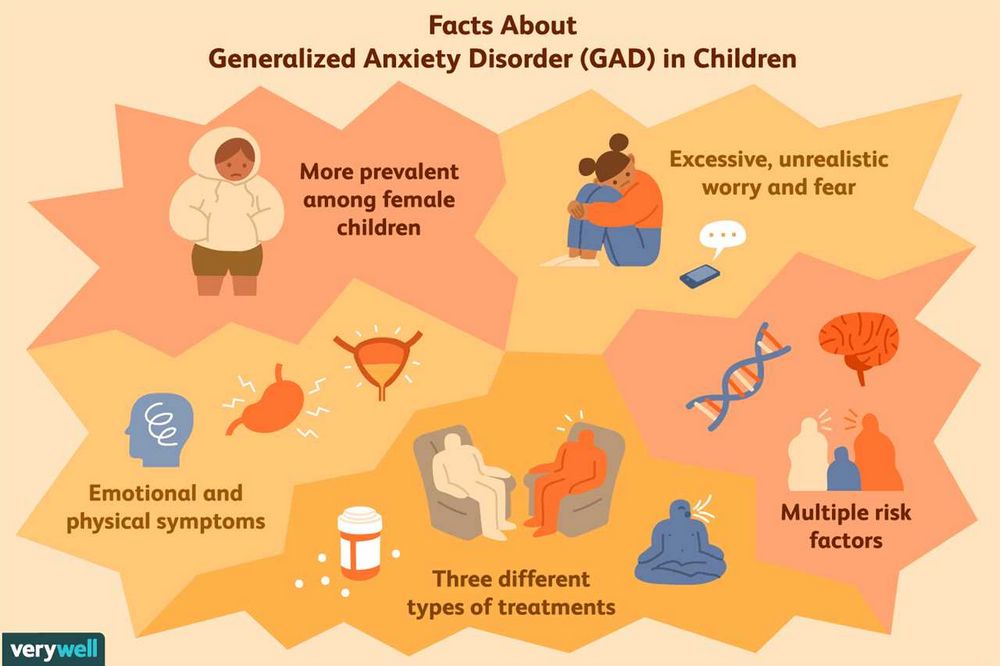
Anxiety can have a significant impact on the mental health of children. It is a common condition that affects many kids, and if left untreated, it can lead to various problems in their lives.
When a child experiences anxiety, it can interfere with their daily activities and relationships. They may have difficulty concentrating in school, participating in social events, or even sleeping at night. Anxiety can also manifest as physical symptoms, such as headaches or stomachaches.
It is important for parents to recognize the signs of anxiety in their children and seek help from a psychiatrist or mental health professional. These professionals can evaluate the child’s symptoms and determine the best course of treatment, which may include therapy, medication, or a combination of both.
Medication, also known as anxiety meds, can be prescribed to children with severe anxiety. These medications can help reduce the symptoms of anxiety and allow the child to function more effectively in their daily life. However, it is important to note that medication should be used as part of a comprehensive treatment plan that includes therapy and support from parents and caregivers.
Therapy is another important component of treating anxiety in children. It provides a safe and supportive environment for the child to express their feelings and learn coping strategies. Through therapy, children can develop skills to manage their anxiety and improve their overall mental well-being.
It is crucial for parents to understand that anxiety is a real and valid condition that can significantly impact their child’s mental health. By seeking professional help and following a comprehensive treatment plan that includes therapy and, if necessary, medication, parents can help their children manage their anxiety and lead happier, healthier lives.
Common Triggers for Anxiety in Kids
Anxiety in children can be triggered by a variety of factors. Understanding these common triggers can help parents and caregivers better support their children’s mental health:
- School-related stress: Academic pressure, social interactions, and performance expectations can all contribute to anxiety in kids. The fear of failure or being judged by peers can be overwhelming for some children.
- Family issues: Conflict, divorce, or other family problems can create a stressful environment for children, leading to anxiety.
- Changes and transitions: Moving to a new home, changing schools, or experiencing other major life changes can trigger anxiety in kids. The uncertainty and fear of the unknown can be particularly challenging for children.
- Health concerns: Chronic illnesses, medical procedures, or the fear of getting sick can all contribute to anxiety in children. The fear of pain or the unknown can be overwhelming for some kids.
- Peer pressure and bullying: Kids may feel anxious due to the pressure to fit in, fear of rejection, or being bullied by their peers. These social dynamics can have a significant impact on a child’s mental well-being.
- Traumatic events: Experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event, such as a car accident or natural disaster, can trigger anxiety in children. The emotional impact of such events can be long-lasting.
It’s important for parents to recognize these triggers and provide appropriate support for their children. This may include seeking professional help from a psychiatrist or therapist, considering medication if necessary, and creating a safe and nurturing environment for kids to express their feelings and concerns.
Treatment Options for Childhood Anxiety

When it comes to treating childhood anxiety, there are several options available to parents and caregivers. These options include medication, therapy, or a combination of both.
One common treatment option is medication, also known as meds. Medication can be prescribed by a psychiatrist or other healthcare professional to help manage anxiety symptoms in children. It is important to note that medication should only be used under the guidance and supervision of a healthcare professional.
Another treatment option is therapy. Therapy can be a valuable tool in helping children with anxiety. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a commonly used approach that focuses on helping children identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors. This type of therapy can be done individually or in a group setting.
In some cases, a combination of medication and therapy may be recommended. This approach can provide a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both the physical and psychological aspects of anxiety.
It is important for parents and caregivers to work closely with healthcare professionals to determine the best treatment option for their child. Each child is unique, and what works for one child may not work for another. Regular communication with the healthcare team is essential to monitor progress and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
| Medication | Therapy | Combination |
|---|---|---|
| Prescribed by a psychiatrist or healthcare professional | Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) | Comprehensive treatment plan |
| Used under guidance and supervision | Individual or group setting | Addresses physical and psychological aspects |
Therapy as a First Line of Treatment

When it comes to treating anxiety in kids, therapy should be considered as the first line of treatment before turning to medication. While medication can be effective in managing anxiety symptoms, it is important to explore non-pharmacological options first.
Therapy, also known as psychotherapy or counseling, involves meeting with a trained mental health professional who can help children learn coping skills, identify triggers, and develop strategies to manage their anxiety. This can be done through various therapeutic approaches, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) or play therapy.
By working with a therapist, children can gain a better understanding of their anxiety and learn techniques to reduce its impact on their daily lives. Therapy can also provide a safe space for children to express their feelings and fears, which can be an important step in their healing process.
While medication may be necessary in some cases, it should not be the first option. It is important to consult with a child psychiatrist or a mental health professional who specializes in working with children before considering medication. They can assess the severity of the anxiety and determine if medication is appropriate.
If medication is prescribed, it is important to closely monitor its effects and any potential side effects. Regular check-ins with the prescribing doctor are essential to ensure the medication is working effectively and to make any necessary adjustments.
Overall, therapy should be the first line of treatment for children with anxiety. It provides a holistic approach to managing anxiety and can empower children to develop lifelong skills for coping with their anxiety. Medication should only be considered when therapy alone is not sufficient in managing the child’s symptoms.
FAQ about topic Anxiety Meds for Kids: What Parents Should Know
What are anxiety meds?
Anxiety meds, also known as anti-anxiety medications, are drugs that are prescribed to help manage symptoms of anxiety disorders in children.
What are the common anxiety meds prescribed for kids?
Common anxiety meds prescribed for kids include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) such as fluoxetine (Prozac) and sertraline (Zoloft), as well as benzodiazepines like diazepam (Valium) and alprazolam (Xanax).
Are anxiety meds safe for children?
Anxiety meds can be safe for children when prescribed and monitored by a healthcare professional. However, it’s important to weigh the potential risks and benefits before starting any medication.
What are the potential side effects of anxiety meds for kids?
Potential side effects of anxiety meds for kids can include drowsiness, dizziness, nausea, headaches, and changes in appetite or weight. It’s important to discuss any concerns with a healthcare professional.
Are there alternative treatments for childhood anxiety?
Yes, there are alternative treatments for childhood anxiety that can be explored before considering medication. These may include therapy, cognitive-behavioral techniques, relaxation exercises, and lifestyle changes.
I am Lena N. Blackwell, a passionate writer and the author behind the content you find on vpequipments.in.
My work covers a range of topics including babies, culture, food, garden, holidays, pregnancy, tips, and travel. I strive to provide valuable insights and information to help parents, families, and individuals navigate through various aspects of life. My goal is to create content that is not only informative but also engaging and relatable, making your journey a little bit easier and more enjoyable.